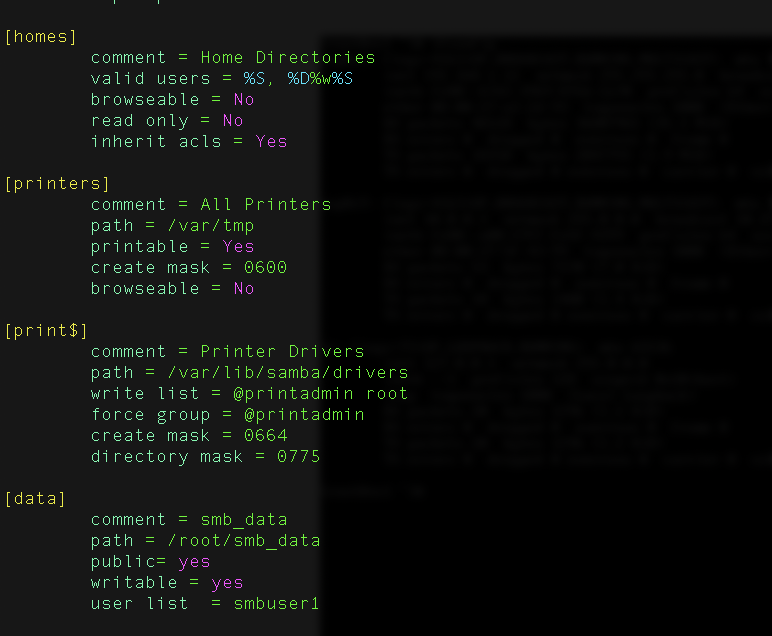
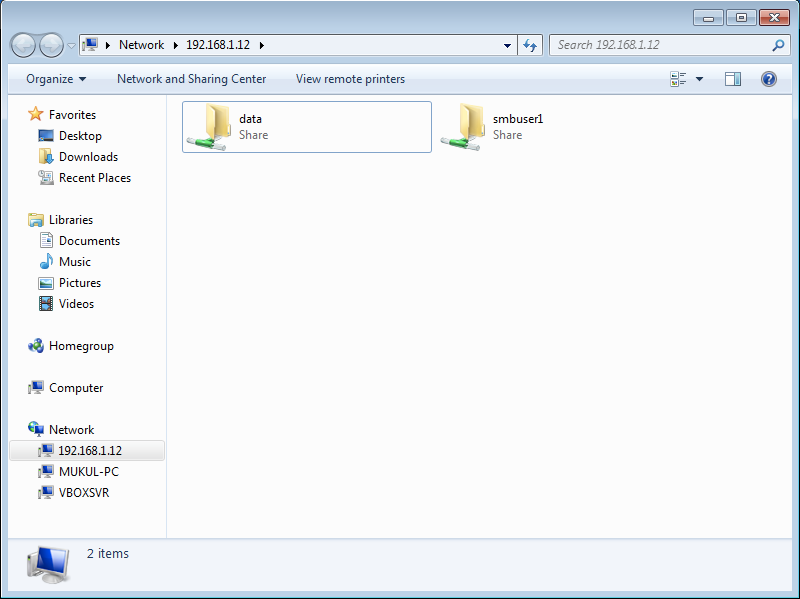
OSCP(offensive security certified professional) in this certification mainly two types of operating systems play an important role in my opinion first is Linux(Server/Client) and the second is Windows(workstation/server). You may encounter other machines with different OS but the probability is very low.
Let’s understand why Linux is the most installed OS in the world, which is mainly because android uses Linux as its OS. It is leading in almost all the market except in the desktop market, where the windows come into play. I know windows covers almost all the Market but Linux as an open source project have its benefits honestly speaking Linux is just the kernel in the GNU/Linux[link] operating system. Many users in the starting find difficult to understand the working as you have done almost all the task manually with terminal whereas on other side windows provide a good GUI interface to interact to do the same task with just one click.
I know if you are a dedicated Linux user it is very unlikely to use windows back again but whether you like or not windows is the most common operating system for the desktop in the current state so as a Pentester or Ethical hacker its necessary to understand windows more you know about it easier for you in future to pentest the machine.
From an infosec point of view, there are two reasons why we should learn Linux. The first is that the majority of all servers in the world are running on Linux based servers and if we are Pentesting a Linux server then we must understand the OS functioning before, the second reason is that the vast majority of all Pentesting tools are only available on Linux based OS especially Kali Linux which is designed for this purpose specially.
In this blog, we look at some of the basics topics of windows machine which i think are necessary to learn and understand the terminology used inside. I am only covering the term which we need to know for this certification because there is lot to cover but this will help you to visualize the bigger picture so without any further delay let's start.
How Much you have to know about windows?
These are topics which i believe you must know about before Pentesting Windows machine.
- CMD
- Powershell and scripting
- Active Directory(*)
- Registry
- Directory structure, File system, and operating system functioning of windows
- Group policies
Let me discuss each one by one.
CMD: command-line interface of windows it is not as powerful as Linux terminal. If you like Linux terminal to do your stuff then you may like Cmd to do your task also. During the Pentesting of windows machine sometimes we only have a command-line interface to interact with machines against GUI it clearly explains its importance as suppose you got a shell of windows client machine but with it, you only have limited functionality then cmd is your best friend for further process.
Group Policies: It is basically the policies which are implemented on a single system or on a group of system, it is one of the main feature of the Active directory. Suppose you have a company with a large number of desktop users using windows machine then how do you think you apply restriction and policies on the system to reduce the workload then Group policies come into play. The basic Strategy is centralized Group Policy administration, which works only in conjunction with Active Directory.
Active Directory: This is the Major topic we should be looking on ‘Active Directory’ organizes company complete hierarchy from which computer belongs on which network to what your profile picture looks like It runs on Windows Server and allows administrators to manage permissions and access to network resources and it also decides which users have access to the storage area. System are present in large numbers and all systems are using AD in almost every sector of IT, therefore, it is important to Understand the AD and how it configures in the windows machine.
Registry: During the enumeration phase of the windows machine we may encounter the Registry. Registry is like a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for windows operating systems meaning the kernel, device, drivers, and services all use the registry to store the key meaning that whenever any program, device, driver and service we configure a new subkey containing settings such as a service’s location, its version, and how to start the program, are all added to the windows registry.
Powershell: Powershell is a command-line shell and scripting language specially made for windows machine to helps windows administrator somewhere similar to bash scripting in Linux we leverage Powershell to run malicious code, with Powershell pentester can stealthy gather internal user data and exploit it. Some of the benefits we get from knowing PowerShell are writing and debugging scripts in Powershell, connecting to windows target, transferring files.
Directory Structure and file system of windows OS: In windows operating system the root directory is usually “C:\” and the directory separator is “\”. \Program Files and \Program Files (x86) are most common directory for Pentester to use.
How much Linux we know for OSCP
This is a nice question there are two things to consider when are Pentesting a machine whether it is Windows or Linux, we always have our Kali Machine to perform Pentesting In ‘ready to hack state’, therefore, consider your kali machine as tools to perform your task on client-side, the point is if you are not able to fully understand your operating system and its tools to perform your task how do you suppose to know that you are doing your job completely, consider this kali as your friend and try to get along with it use on regular basis try to get familiar with it. its feel difficult in starting but as time goes on eventually you like Linux more than other OS
So this debian-derived Linux distribution is all we have, deep knowledge of kali is always pays off to Pentester in future. The second case is when we encounter Linux machine in client-side as a server commonly(Red Hat Enterprise Linux) or maybe as workstation during Pentesting.
For Further knowing about Kali Linux refer to Knowing kali post.