Security-Enhanced Linux as its name suggests it is security enhancement in Red Hat distribution. As we know in Linux the main benefit is that we can modify the kernel according to our needs and make our own flavor. So SELinux is a kernel module(Centos) with more security by more security I mean access control security.
Before the introduction of SELinux which works on Mandatory access control(MAC), Discretionary access control was used.
The DAC means the access control is based on the file owner and its permission. The root user has full access control with a DAC system.
If the system is a normal workstation then using the DAC may be a good choice but if it a Red Hat-based Linux server the use of DAC is not a good practice. Giving all access control to one user is not advisable.
But after the MAC policy introduction by SELinux, there is an administratively prebuilt policy for access means if the DAC policy or its setting changes on the file, directory then SELinux policies are there to prevent the misuse of permission. Of course, SELinux gives flexibility to limit access between users for files, directory, and more. So, now comes the benefits of this hole thing we discussed, suppose you are running a Linux server(centos) with disable SELinux on it. if Your Linux server hosting many webpages and website, if any hacker can gain access through one of the vulnerability on these website vulnerabilities like
1. Web ports HTTP(80) and https(443)
2. File transfer services FTP or proftpd
3. Through ssh service
4. Vulnerable plugin and theme installed on the website
After finding vulnerability first approach hackers is to put the shell inside the web server and gain the reverse shell to get the root access if we use old access policy like DAC then our hole server compromises and it makes easier for the hacker to do his job but with SELinux, there are some changes to protect our server. SELinux isolates the working of processes run by the local user to remove this type of chance of privilege escalation. The policies used by Mandatory access control are prebuilt we can’t change it but can make custom policy according to our needs.
Configuration files of SELinux
There are two methods to configure the config file SELinux
1. Using GUI: You can access GUI through
system>Administrator>SELinux management
2. Manually via config file
You can directly access the config file using any text editor like vim
using the location /etc/selinux/config
Before the introduction of SELinux which works on Mandatory access control(MAC), Discretionary access control was used.
The DAC means the access control is based on the file owner and its permission. The root user has full access control with a DAC system.
If the system is a normal workstation then using the DAC may be a good choice but if it a Red Hat-based Linux server the use of DAC is not a good practice. Giving all access control to one user is not advisable.
But after the MAC policy introduction by SELinux, there is an administratively prebuilt policy for access means if the DAC policy or its setting changes on the file, directory then SELinux policies are there to prevent the misuse of permission. Of course, SELinux gives flexibility to limit access between users for files, directory, and more. So, now comes the benefits of this hole thing we discussed, suppose you are running a Linux server(centos) with disable SELinux on it. if Your Linux server hosting many webpages and website, if any hacker can gain access through one of the vulnerability on these website vulnerabilities like
1. Web ports HTTP(80) and https(443)
2. File transfer services FTP or proftpd
3. Through ssh service
4. Vulnerable plugin and theme installed on the website
After finding vulnerability first approach hackers is to put the shell inside the web server and gain the reverse shell to get the root access if we use old access policy like DAC then our hole server compromises and it makes easier for the hacker to do his job but with SELinux, there are some changes to protect our server. SELinux isolates the working of processes run by the local user to remove this type of chance of privilege escalation. The policies used by Mandatory access control are prebuilt we can’t change it but can make custom policy according to our needs.
Configuration files of SELinux
There are two methods to configure the config file SELinux
1. Using GUI: You can access GUI through
system>Administrator>SELinux management
2. Manually via config file
You can directly access the config file using any text editor like vim
using the location /etc/selinux/config
 |
| Command to edit config file |
After the modification in config file we need to reboot the system and after that login to your system and view the cat /var/log/messages if you do not see any error then all is fine and all MAC policy are implemented successfully but if you observer any error then the chances are policy is not implemented successfully.
When SELinux denies an action an Access vector is generated called AVC(access vector cache) which shows its message to /var/log/audit/audit.log and /var/log/messages, for troubleshooting use research to find any recent AVC messages.
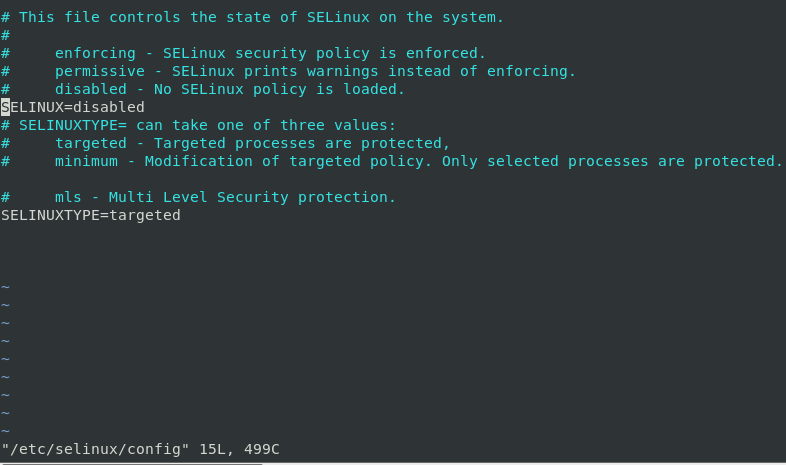 |
| Config file of SELinux |
There are three basic mode for SELinux
Permissive: SELinux is enabled but the MAC policies that are not enforcing on the system only the warring to the user shows and a log of it displays.
Enforcing: The default mode, strict mode enabling all policies and restrictions on the system.
Disabled: The default mode which is mainly present on the system, SELinux is off in this mode.
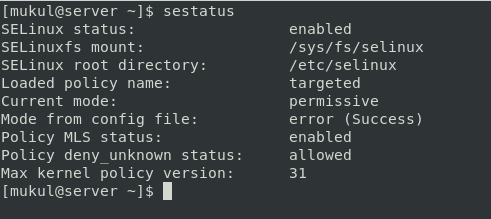
We can view the status of the current running mode of SELinux before editing the config file through “SEStatus”
| SEStatus |
Inside the config file, we also see SELINUXTYPE this option is used to set policy type which you want to use the default one is Targeted policy
Targeted: default one which implements all the MAC policy(most restricted)
Minimum: Only selected processes are protected we have the liberty of modification of some targeted made policy
Mis: server follows Multi-level security protection to prevent users from obtaining access to information for which they don’t authorize.
SELinux Policy Overview:
In the SELinux policy, there are 700 main topics with approx. 10 lakh permission defined already inside “policy.config file”. It is a very large size life so it is obvious that policy ensures the safety of all services which run inside the system from this. It seems the local administrator cannot make such a huge policy himself for system security to satisfy the security needs.
 |
| Status file after enabling SELinux |
SELinux policies are developed in such a manner that all applications cover at least one policy or more. The policy is design in such method that all measure which used to enable the service and configure the service is at his highest level if the user or any domain user wants to run the service apart from his scope user must have to change the policy means we can think that lowest policy privileges are given to the local user. SELinux policy is not only to protect user-level thread but also kernel-level thread and its classes.
SELinux supports a variety of access control models among them main focus was on extended type enforcement.
 |
| Type_enforcement_model_in_Selinux |
In the type enforcement model, set off operation represented by an object of any class with data types. Permission on each operation and its associated classes are different in fact each object of the different class have different permission on it then it is up to administrator how to manage permission of object of different classes.
The main difference between the old and new policy is set off rules that define the security and access right for process in the system. An SELinux predefined policy for users, group and other for accessing to roles, role access to their domain
SELinux introduced the predefined users, the users we create on the system are linked to one or more SELinux domain the basic roles of users are allowed to users plus one advantage is that process which is running by the local user are mapped to the predefined policy or we can say role allowed to the user. The definition of role in SELinux policy defines which users have access right to what role.
Sometimes, the pre-built policy makes hard for administrator and local users to use the system and resolve an issue regarding policy therefore the only remaining option is to choose permissive SELinux mode.



No comments:
Post a Comment